Question Number: 68
PDR Number: SQ22-000198
Date Submitted: 07/11/2022
Department or Body: Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water
Under the step change scenario in the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO)’s 2022 Integrated System Plan (ISP), the renewable share of total annual generation is projected to increase to 83 per cent by 2030-31. The ISP notes that the step change scenario closely aligns with the Australian Government’s legislated 2030 target of reducing emissions by 43 per cent of 2005 levels.
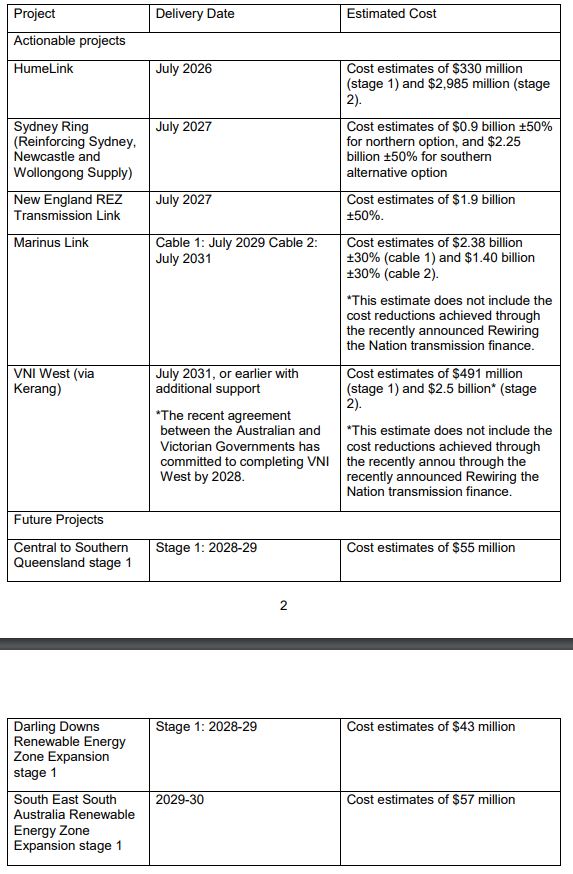
2 The step change scenario indicates approximately 4,000 km of new transmission will be required by 2030, and around 10,000 kilometres by 2050 (see figure 28 on page 63 of the 2022 ISP). This amount is an estimate based on the 2022 AEMO ISP and is therefore limited to transmission within the National Electricity Market (NEM). The 2022 ISP modelling does not include the Queensland Energy and Jobs Plan (which was announced after the release of the ISP), or transmission projects in Western Australia and the Northern Territory that may support the Commonwealth’s emissions reduction targets. Several major transmission projects are already underway and will be in place by the mid-2020s, including the Central West Orana Renewable Energy Zone Transmission Link in NSW, Project Energy Connect between NSW and South Australia, and the Western Renewables Link in Victoria. In addition the ISP includes detailed cost estimates for actionable and future ISP projects and modelling of the total estimated costs and benefits out to 2050. The following table provides the costs estimates for actionable and future projects in the 2022 ISP which are expected to be in delivered by 2030: See table.